Building fire safety regulatory assessment
Place
Focus
Status
Outputs
What it is
Overview
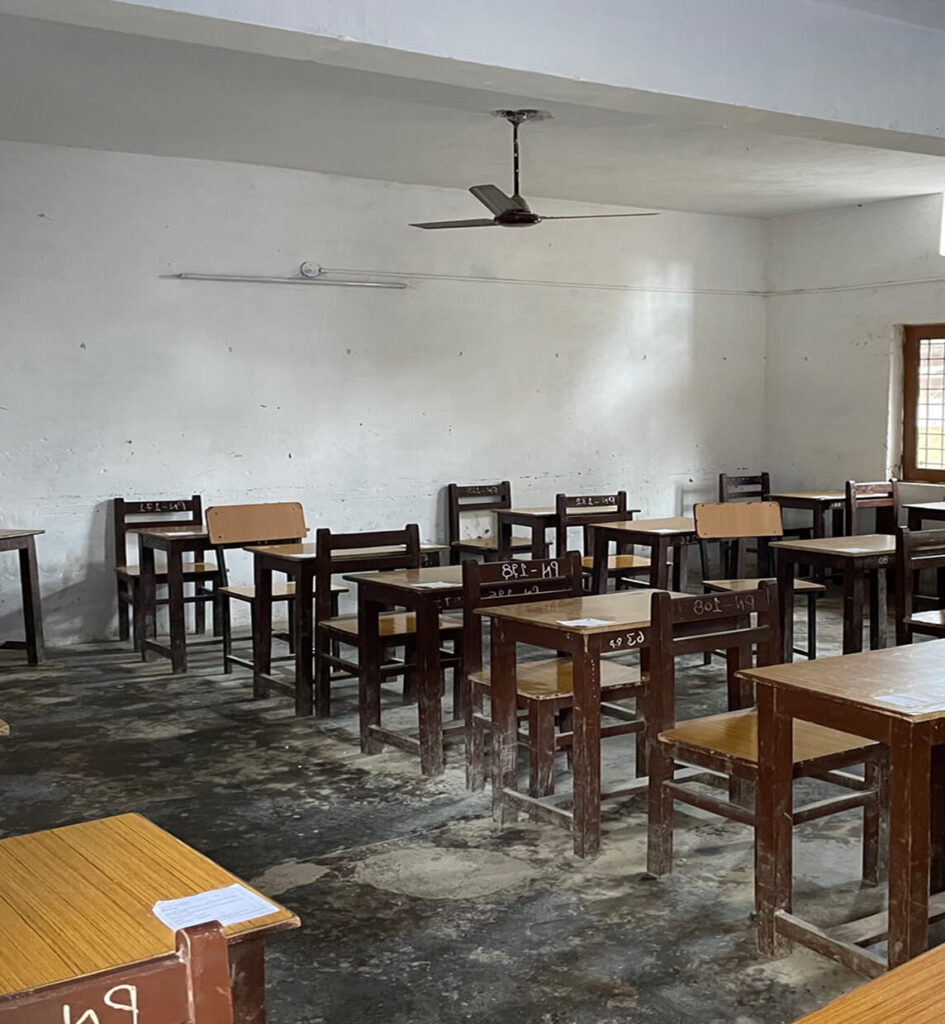
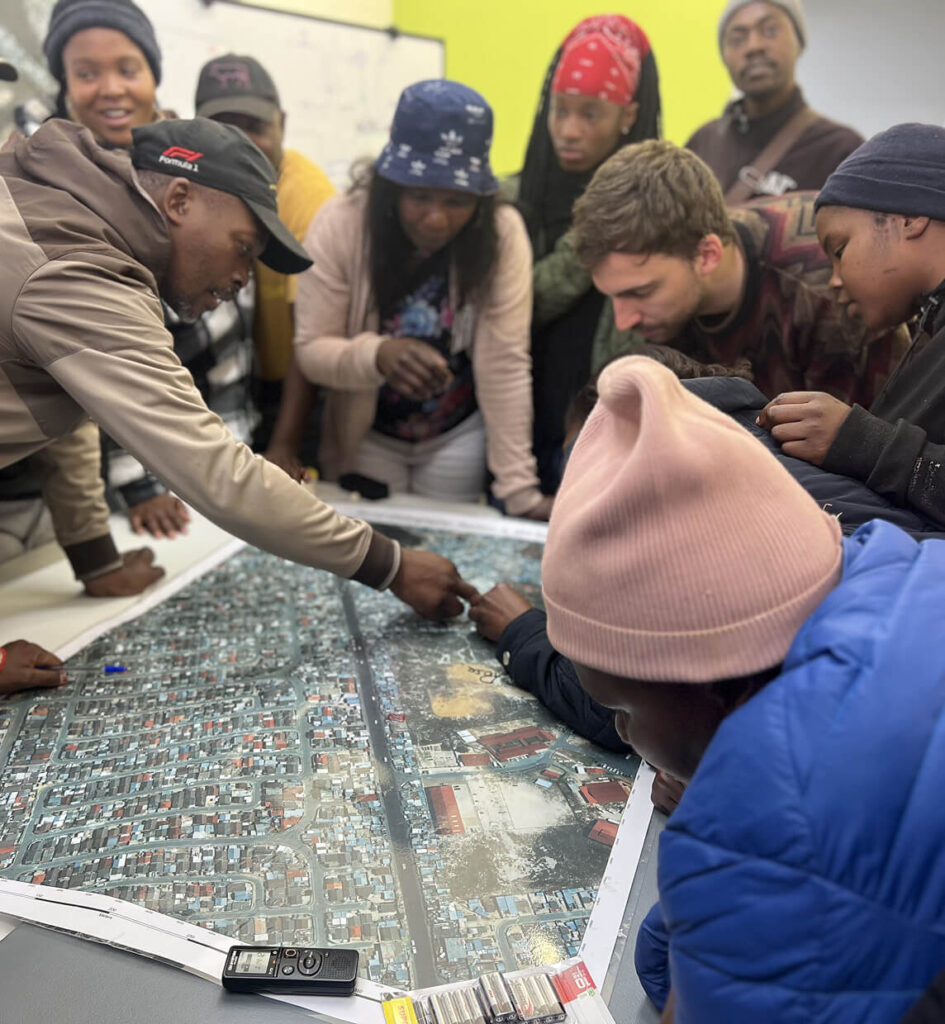
Kindling partnered with the World Bank to examine how regulatory and institutional systems shape fire safety outcomes in the built environment in Uttarakhand, India.
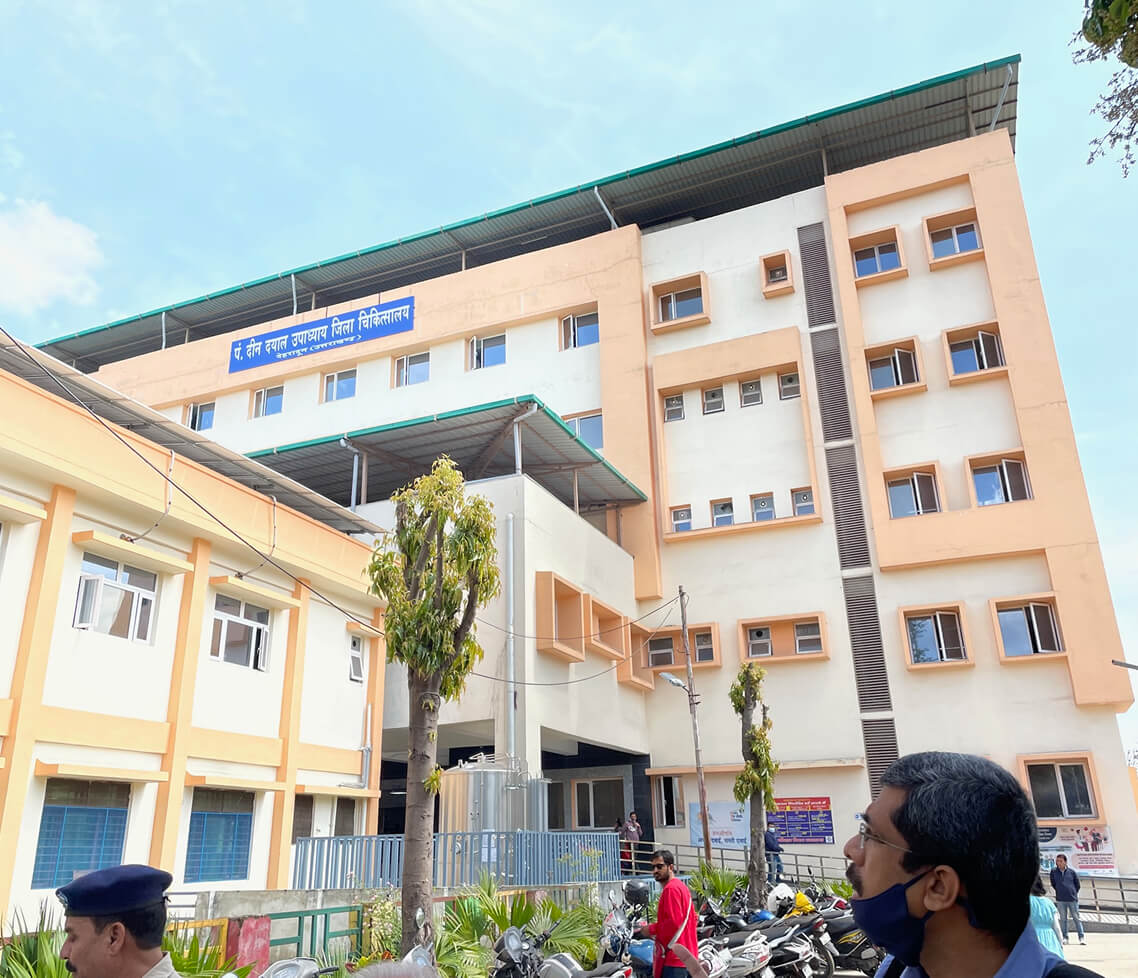
The study focused on how governance, regulation, and implementation interact in practice, using schools and hospitals as key lenses to assess how fire safety provisions are applied and maintained.
The work identified opportunities to strengthen institutional capacity, technical competence, and accountability frameworks essential for protecting lives.
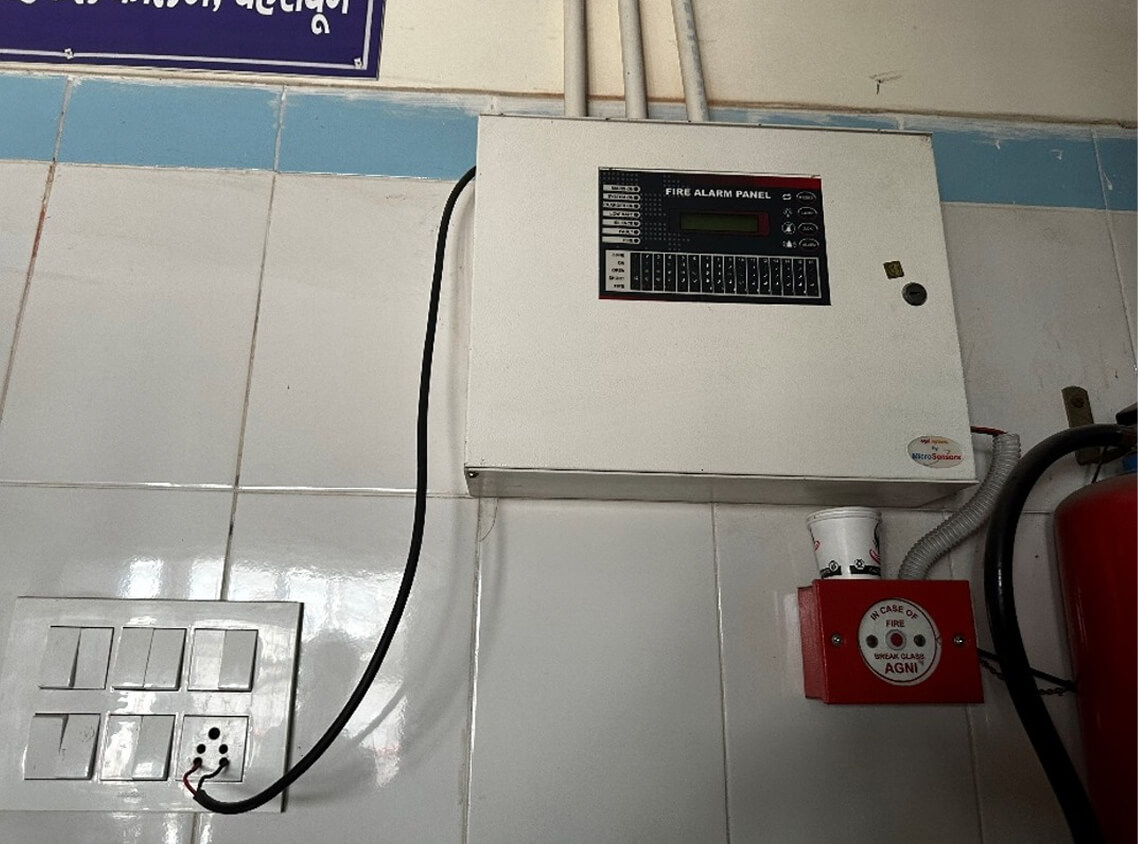

“Emphasis is placed on the presence of fire safety equipment rather than on its performance and maintenance, undermining fire safety. ”
- Danielle Antonellis
Fire Engineer
The challenge
Across many rapidly urbanizing contexts, building regulations exist on paper but are inconsistently applied in practice. Fragmented governance, limited inspection capacity, and uneven professional training often leave gaps between what codes require and what communities experience.
Fire safety is particularly vulnerable to these systemic weaknesses. Even when technical standards are sound, the absence of clear accountability, resourcing, and maintenance frameworks can undermine the protection they are meant to provide.

Our Approach
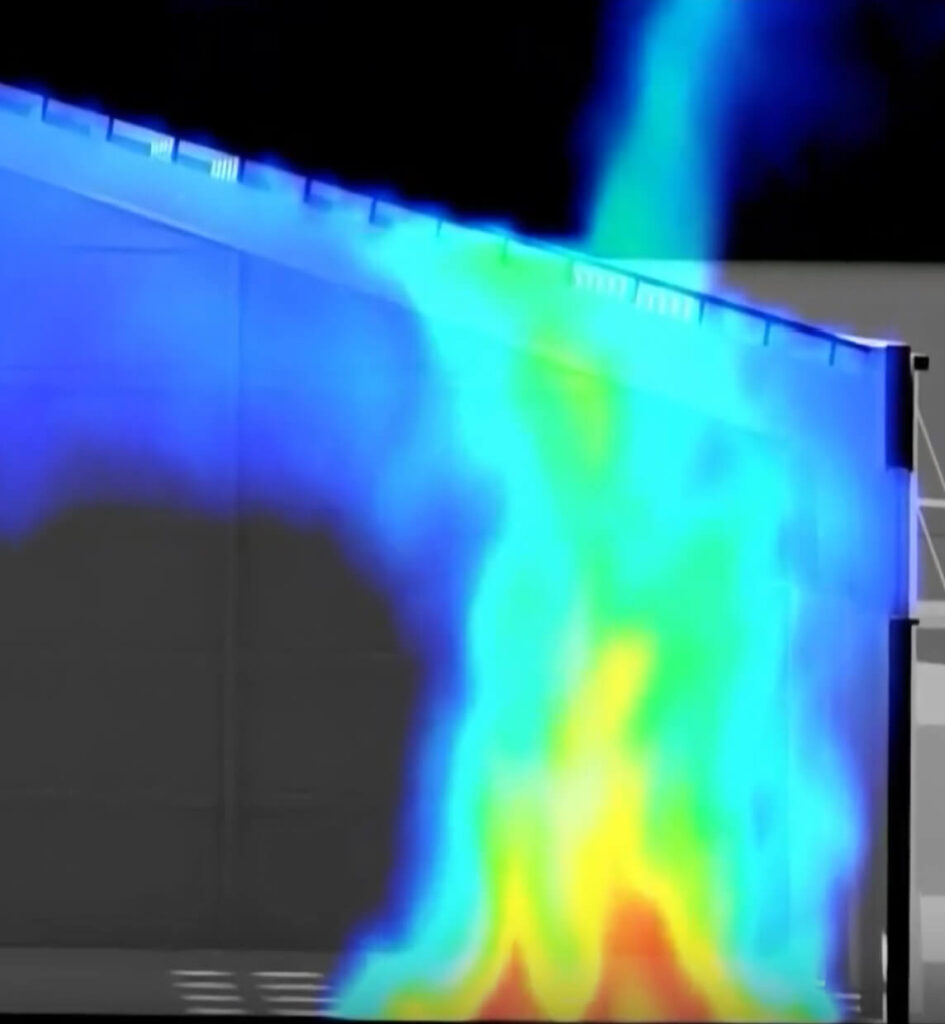
For our work in India, we applied a suite of diagnostic tools developed by the World Bank, including the Urban Fire Regulatory Assessment and Mitigation Evaluation (Urban FRAME) and the Building Code Checklist for Fire Safety. These frameworks provided a structured way to analyze how governance systems, institutional coordination, and technical standards influence the implementation of fire and life safety measures.
The assessment combined policy and document review, site inspections of case study hospitals and schools, and consultations with government officials to understand how fire safety provisions are interpreted and enforced in practice. This multi-layered approach enabled the team to identify not only technical and procedural gaps but also the institutional and cultural factors that shape everyday safety outcomes.
Strengthening Fire Safety Systems
The analysis showed that improving fire safety depends as much on governance and institutional culture as on technical code content. Strengthening outcomes requires:
- Clearer coordination across government levels and agencies;
- Investment in professional capacity and certification;
- Maintenance and inspection systems that ensure long-term performance; and
- Evidence-based diagnostics to guide reform and track progress.
Taken together, these findings underscore that fire safety regulation is a cornerstone of resilient, inclusive development. By linking policy, institutions, and practice, this collaboration revealed how systemic approaches can uncover structural barriers to safety and chart practical pathways for reform.
Applying this kind of systems-based analysis can help governments and development partners identify practical entry points for reform, prioritize investments, and embed fire resilience within broader urban development agendas.
Project Sponsor
This project was made possible through a Technical Assistance grant from the World Bank.